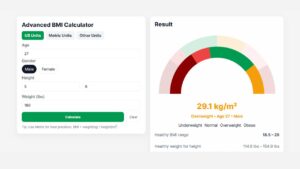
Advanced BMI Calculator: Accurate Body Mass Index & Health Insights
An Advanced BMI Calculator is a modern upgrade to the traditional Body Mass Index tool, designed for more accurate health assessment. The advanced version bridges this gap by integrating additional metrics such as waist-to-height ratio, body fat percentage, and ethnicity-based adjustments. This makes it far more reliable for identifying potential health risks and guiding fitness goals. Whether you’re an athlete, someone managing weight, or simply tracking your wellness, an advanced BMI calculator provides a personalized, data-driven insight that goes beyond a single number, helping you make informed lifestyle decisions.
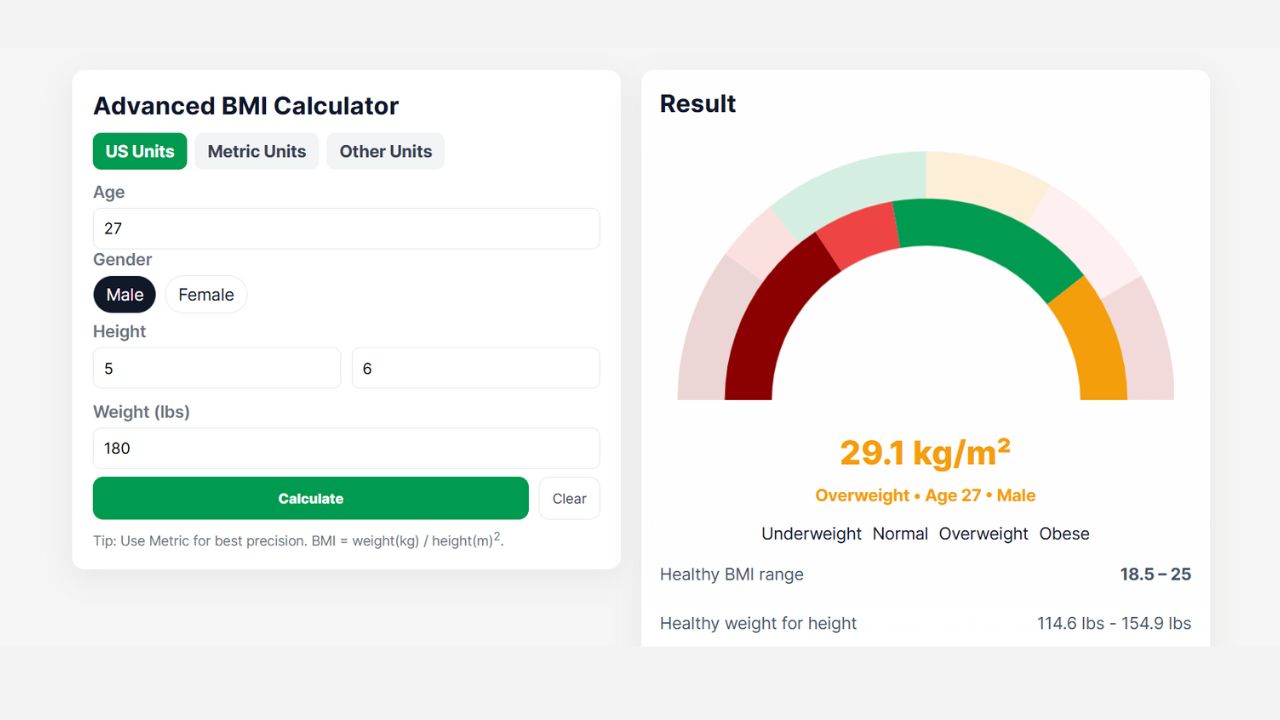
Advanced BMI Calculator
Result
Understanding the Advanced BMI Calculator and Its Formula
The Advanced BMI Calculator is an upgraded version of the traditional Body Mass Index tool, designed to give you a more accurate picture of your health. The standard BMI formula is:
BMI = weight (kg) / [height (m)]²
While this formula has been used for decades, it has one major limitation—it treats everyone the same, regardless of factors like age, gender, muscle mass, and ethnicity. The advanced version fixes this by adding extra data points to deliver personalized results.
Instead of simply telling you whether you are underweight, normal, overweight, or obese, an Advanced BMI Calculator can also consider body fat percentage, waist-to-height ratio, and even fitness level. This means an athlete with high muscle mass won’t be unfairly classified as “overweight,” and individuals from different ethnic backgrounds get results that match their health risk profiles more accurately.
By using a more refined method, this calculator transforms BMI from a basic weight-to-height ratio into a comprehensive health insight tool. Whether you’re on a fitness journey, monitoring weight changes, or simply curious about your health, the advanced approach gives you a reliable starting point for smarter lifestyle choices.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Use an Advanced BMI Calculator Effectively
Using an Advanced BMI Calculator is simple, but getting accurate results requires the right approach.
- Prepare Your Measurements – Accurately measure your height, weight, and waist circumference. Use a reliable scale and a flexible tape measure.
- Enter Additional Data – Fill in details like age, gender, and activity level if prompted. Some calculators also ask for body fat percentage.
- Submit the Information – Click the calculate button to get your BMI score along with extended health metrics.
- Review the Results – Look beyond just the BMI number. Check your waist-to-height ratio, body fat percentage, and any health recommendations provided.
- Interpret in Context – Compare your results with healthy ranges for your demographic. If your BMI is slightly high but your fat percentage is low, muscle mass may be the reason.
- Take Action – Use the results to adjust your diet, exercise, or lifestyle as needed.
By following these steps, you ensure that the results you get from an Advanced BMI Calculator are not only accurate but also meaningful for long-term health planning.
Why the Traditional BMI Formula Falls Short
The traditional BMI formula has been a global standard since the 19th century, but modern science has revealed its flaws. Its biggest limitation is that it doesn’t distinguish between fat and muscle. A bodybuilder, for example, could have a high BMI but a very low body fat percentage. Conversely, someone with a “normal” BMI could have unhealthy levels of body fat—known as “skinny fat”—which still carries serious health risks.
Another shortcoming is that it ignores age, gender, and ethnicity. Women naturally carry more body fat than men, and some ethnic groups are at higher risk for obesity-related conditions at lower BMI thresholds. Yet, the traditional method applies the same categories to everyone, making it inaccurate for large segments of the population.
Furthermore, the standard BMI doesn’t account for fat distribution. Visceral fat around the abdomen poses more health risks than fat in other areas, but BMI alone can’t measure that.
This is where the Advanced BMI Calculator comes in—by incorporating extra variables, it delivers insights that are far more relevant and reliable. In short, while traditional BMI can provide a rough idea of weight status, it’s outdated for precise health analysis.
Key Features of an Advanced BMI Calculator
An Advanced BMI Calculator is built for accuracy, personalization, and usability. Its standout features include:
- Multiple Data Inputs – Instead of just height and weight, it can take age, gender, waist circumference, and body fat percentage for a deeper assessment.
- Ethnicity-Based Adjustments – Recognizes that BMI thresholds vary across populations for better risk prediction.
- Fat Distribution Analysis – Includes waist-to-height ratio or waist-to-hip ratio to highlight abdominal fat risks.
- Fitness Level Consideration – Differentiates between high muscle mass and high fat mass to avoid misclassification.
- Interactive User Interface – Clear result displays, color-coded health ranges, and easy-to-read charts for instant understanding.
- Custom Health Recommendations – Some advanced calculators offer nutrition and exercise suggestions based on results.
These features make the advanced version not just a measurement tool, but an educational resource. It encourages users to take a proactive approach toward health rather than relying solely on a number.
By combining traditional BMI principles with modern health metrics, the advanced version offers a holistic view of your body’s condition. It’s not just about where you are today—it’s about giving you the knowledge to shape your future health.
Check Out Those Useful Articles
How to Create a BMI Calculator using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript
Creating a BMI Calculator with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript is an excellent project for learning web development.
To BMI Calculator follow these steps:
- Create a Folder: Name this folder according to your preference. Inside this folder, you’ll need to set up the following files:
- Create an index.html File: This file should be named index with the .html extension.
- Create a style.css File: This file should be named style with the .css extension.
- Create a script.js File: This file should be name main with the .js extension.
These files will form the basis of your BMI Calculator.
Writing the HTML Structure for the BMI Calculator
Now, open your code editor and set up a new HTML file, copy those HTML Codes and Paste those Codes on index.html file.
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1" />
<title>Advanced BMI Calculator (no needle)</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/chart.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="page">
<div class="wrap">
<!-- LEFT -->
<div class="panel" aria-labelledby="title">
<h1 id="title">Advanced BMI Calculator</h1>
<div class="tabs" role="tablist">
<div class="tab active" id="tab-us">US Units</div>
<div class="tab" id="tab-metric">Metric Units</div>
<div class="tab" id="tab-other">Other Units</div>
</div>
<label>Age</label>
<input id="age" type="number" min="2" max="120" value="27">
<label>Gender</label>
<div class="gender-wrap">
<div class="gender-btn active" id="gender-male">Male</div>
<div class="gender-btn" id="gender-female">Female</div>
</div>
<!-- US -->
<div id="panel-us">
<label>Height</label>
<div class="row">
<input id="ft" class="xsmall" type="number" value="5" min="3" max="8">
<input id="inch" class="xsmall" type="number" value="6" min="0" max="11">
</div>
<label>Weight (lbs)</label>
<input id="lbs" type="number" value="180">
</div>
<!-- Metric -->
<div id="panel-metric" style="display:none">
<label>Height (cm)</label>
<input id="cm" type="number" value="180">
<label>Weight (kg)</label>
<input id="kg" type="number" value="95">
</div>
<!-- Other -->
<div id="panel-other" style="display:none">
<label>Height (m)</label>
<input id="m" type="number" step="0.01" placeholder="1.80">
<label>Weight (kg)</label>
<input id="kg2" type="number" placeholder="78">
</div>
<div class="actions">
<button class="calc" id="calcBtn">Calculate</button>
<button class="clear" id="clearBtn" type="button">Clear</button>
</div>
<div class="hint">Tip: Use Metric for best precision. BMI = weight(kg) / height(m)<sup>2</sup>.</div>
</div>
<!-- RIGHT -->
<div class="results" aria-live="polite">
<h1 id="title">Result</h1>
<div class="gauge-wrap">
<div class="gauge-holder"><canvas id="gauge" aria-label="BMI gauge"></canvas></div>
<div class="bmi-large" id="bmiValue">--</div>
<div class="category" id="bmiCat">—</div>
<div class="legend">
<div class="item"><span class="sw" style="background:var(--under)"></span>Underweight</div>
<div class="item"><span class="sw" style="background:var(--normal)"></span>Normal</div>
<div class="item"><span class="sw" style="background:var(--over)"></span>Overweight</div>
<div class="item"><span class="sw" style="background:var(--obese)"></span>Obese</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="summary">
<div class="row"><div>Healthy BMI range</div><div><strong>18.5 – 25</strong></div></div>
<div class="row"><div>Healthy weight for height</div><div id="healthyRange">—</div></div>
<div class="row"><div>Change to reach BMI 25</div><div id="to25">—</div></div>
<div class="row"><div>BMI Prime</div><div id="prime">—</div></div>
<div class="row"><div>Ponderal Index</div><div id="ponderal">—</div></div>
</div>
<footer class="note">Animated semicircle gauge • responsive • Chart.js • (no needle)</footer>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script src="script.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Styling the BMI Calculator Using CSS
After that, copy those CSS Codes and Paste those Codes on style.css file.
:root {
--bg:#f5f7fb;
--card:#fff;
--accent:#009a50;
--muted:#6b7280;
--under:#b91c1c;
--under2:#e11d48;
--normal:#009a50;
--over:#f59e0b;
--obese:#b91c1c;
}
* {
box-sizing: border-box;
font-family: Inter, system-ui, Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
}
body {
margin: 0;
background: #f5f5f5;
padding: 28px;
color: #0f172a;
}
.page {
max-width: 1100px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.wrap {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: 1fr 50%;
gap: 20px;
align-items: flex-start;
}
@media (max-width: 980px) {
.wrap { grid-template-columns: 1fr; }
}
.panel {
background: var(--card);
padding: 20px;
border-radius: 12px;
box-shadow: 0 8px 28px rgba(15,23,42,0.06);
}
h1 {
margin: 0 0 12px;
font-size: 24px;
}
.tabs {
display: flex;
gap: 8px;
margin-bottom: 12px;
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
.tab {
padding: 8px 12px;
border-radius: 8px;
background: #f3f4f6;
color: #374151;
cursor: pointer;
font-weight: 700;
}
.tab.active {
background: var(--accent);
color: #fff;
}
label {
display: block;
color: var(--muted);
font-weight: 600;
margin-bottom: 6px;
}
.row {
display: flex;
gap: 10px;
align-items: center;
margin-bottom: 12px;
}
input[type="number"], select {
width: 100%;
padding: 10px;
border-radius: 8px;
border: 1px solid #e6e9ee;
font-size: 15px;
background: #fff;
}
.two { flex: 1; }
.xsmall { width: 88px; }
.gender-wrap {
display: flex;
gap: 8px;
margin-bottom: 8px;
}
.gender-btn {
padding: 8px 12px;
border-radius: 999px;
border: 1px solid #e6e9ee;
background: #fff;
cursor: pointer;
}
.gender-btn.active {
background: #111827;
color: #fff;
}
.actions {
display: flex;
gap: 10px;
margin-top: 8px;
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
button.calc {
flex: 1;
padding: 12px;
border-radius: 10px;
border: none;
background: var(--accent);
color: #fff;
font-weight: 800;
cursor: pointer;
}
button.clear {
padding: 12px;
border-radius: 10px;
border: 1px solid #e6e9ee;
background: #fff;
color: #374151;
cursor: pointer;
}
.hint {
font-size: 13px;
color: var(--muted);
margin-top: 10px;
}
/* Right results */
.results {
background: linear-gradient(180deg,rgba(255,255,255,0.95),#fff);
padding: 18px;
border-radius: 12px;
box-shadow: 0 8px 28px rgba(15,23,42,0.06);
}
.gauge-wrap {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
gap: 12px;
}
.gauge-holder {
width: 100%;
max-width: 480px;
height: 280px;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
canvas#gauge {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
opacity: 0;
transition: opacity .32s;
}
canvas#gauge.visible {
opacity: 1;
}
.bmi-large {
font-size: 32px;
font-weight: 800;
color: #0f172a;
}
.category {
font-size: 16px;
font-weight: 700;
color: var(--muted);
}
.legend {
display: flex;
gap: 10px;
flex-wrap: wrap;
justify-content: center;
margin-top: 6px;
}
.sw {
width: 14px;
height: 14px;
border-radius: 3px;
}
.summary {
margin-top: 12px;
}
.summary .row {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
padding: 8px 0;
color: #475569;
}
footer.note {
text-align: center;
color: var(--muted);
font-size: 13px;
margin-top: 8px;
}
@media (max-width: 520px) {
.bmi-large { font-size: 24px; }
.gauge-holder { height: 220px; }
body { padding: 14px; }
}
Adding JavaScript for BMI Calculator
And lastly, Copy the below JS code and paste it into the script.js file.
/* -------------------------
DOM refs & state
------------------------- */
const tabUs = document.getElementById('tab-us');
const tabMetric = document.getElementById('tab-metric');
const tabOther = document.getElementById('tab-other');
const panelUs = document.getElementById('panel-us');
const panelMetric = document.getElementById('panel-metric');
const panelOther = document.getElementById('panel-other');
tabUs.addEventListener('click', ()=>switchUnit('us'));
tabMetric.addEventListener('click', ()=>switchUnit('metric'));
tabOther.addEventListener('click', ()=>switchUnit('other'));
let unit = 'us';
function switchUnit(u){
unit = u;
tabUs.classList.toggle('active', u==='us');
tabMetric.classList.toggle('active', u==='metric');
tabOther.classList.toggle('active', u==='other');
panelUs.style.display = u==='us' ? '' : 'none';
panelMetric.style.display = u==='metric' ? '' : 'none';
panelOther.style.display = u==='other' ? '' : 'none';
}
const genderMale = document.getElementById('gender-male');
const genderFemale = document.getElementById('gender-female');
let gender = 'male';
genderMale.addEventListener('click', ()=>setGender('male'));
genderFemale.addEventListener('click', ()=>setGender('female'));
function setGender(g){ gender = g; genderMale.classList.toggle('active', g==='male'); genderFemale.classList.toggle('active', g==='female'); }
/* inputs */
const ageEl = document.getElementById('age');
const ftEl = document.getElementById('ft');
const inEl = document.getElementById('inch');
const lbsEl = document.getElementById('lbs');
const cmEl = document.getElementById('cm');
const kgEl = document.getElementById('kg');
const mEl = document.getElementById('m');
const kg2El = document.getElementById('kg2');
const calcBtn = document.getElementById('calcBtn');
const clearBtn = document.getElementById('clearBtn');
const bmiValueEl = document.getElementById('bmiValue');
const bmiCatEl = document.getElementById('bmiCat');
const healthyRangeEl = document.getElementById('healthyRange');
const to25El = document.getElementById('to25');
const primeEl = document.getElementById('prime');
const ponderalEl = document.getElementById('ponderal');
const canvas = document.getElementById('gauge');
/* -------------------------
Gauge - zones & chart
------------------------- */
const minBMI = 10;
const maxBMI = 40;
const totalRange = maxBMI - minBMI;
/* zones copying screenshot proportions (approx widths) */
const zones = [
{ label:'Under 16', from: minBMI, to:16, color: '#8b0000' }, // deep red
{ label:'16-18.5', from:16, to:18.5, color: '#ef4444' }, // lighter red
{ label:'18.5-25', from:18.5, to:25, color: getComputedStyle(document.documentElement).getPropertyValue('--normal') || '#2ecc71' },
{ label:'25-30', from:25, to:30, color: getComputedStyle(document.documentElement).getPropertyValue('--over') || '#f59e0b' },
{ label:'30-35', from:30, to:35, color: '#fca5a5' },
{ label:'35-40', from:35, to:40, color: getComputedStyle(document.documentElement).getPropertyValue('--obese') || '#b91c1c' },
];
const zoneSizes = zones.map(z => z.to - z.from);
/* Chart state */
let chart = null;
let animRAF = null;
let currentSegments = zones.map(()=>0);
/* create chart skeleton */
function createChart(){
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
const baseDataset = {
label: 'base',
data: zoneSizes.slice(),
backgroundColor: zones.map(z => hexToRgba(z.color, 0.16)),
borderWidth: 0
};
const fillDataset = {
label: 'fill',
data: zones.map(_=>0),
backgroundColor: zones.map(z => z.color),
borderWidth: 0
};
if(chart) chart.destroy();
chart = new Chart(ctx, {
type: 'doughnut',
data: {
labels: zones.map(z=>z.label),
datasets: [baseDataset, fillDataset]
},
options: {
responsive:true,
maintainAspectRatio:false,
rotation: 270,
circumference: 180,
cutout: '62%',
plugins: { legend:{display:false}, tooltip:{enabled:false} },
animation: { duration: 0 }
}
});
canvas.classList.remove('visible');
}
createChart();
function hexToRgba(hex,a=1){
hex = (hex||'#000').replace('#','').trim();
if(hex.length===3) hex = hex.split('').map(c=>c+c).join('');
const r = parseInt(hex.slice(0,2),16);
const g = parseInt(hex.slice(2,4),16);
const b = parseInt(hex.slice(4,6),16);
return `rgba(${r},${g},${b},${a})`;
}
/* compute amount per zone from BMI value */
function computeFillSegments(bmi){
let remain = clamp(bmi - minBMI, 0, totalRange);
return zones.map(z=>{
const length = Math.max(0, Math.min(remain, z.to - z.from));
remain -= length;
return length;
});
}
/* animate fill segments smoothly */
function easeOutCubic(t){ return 1 - Math.pow(1 - t, 3); }
function animateTo(targetSegments, duration=900){
if(animRAF) cancelAnimationFrame(animRAF);
const start = performance.now();
const from = currentSegments.slice();
function step(now){
const t = Math.min(1, (now - start)/duration);
const e = easeOutCubic(t);
const cur = from.map((v,i)=> v + (targetSegments[i] - v) * e);
currentSegments = cur;
chart.data.datasets[1].data = cur;
chart.update('none');
if(t < 1) animRAF = requestAnimationFrame(step);
else { animRAF = null; currentSegments = targetSegments.slice(); }
}
animRAF = requestAnimationFrame(step);
}
/* clamp */
function clamp(v,a,b){ return Math.max(a, Math.min(b, v)); }
/* -------------------------
Calculation logic
------------------------- */
function toMetric(){
let weightKg, heightM;
if(unit === 'metric'){
weightKg = parseFloat(kgEl.value) || NaN;
heightM = (parseFloat(cmEl.value) || NaN) / 100;
} else if(unit === 'us'){
const ft = parseFloat(ftEl.value) || 0;
const inch = parseFloat(inEl.value) || 0;
const totalIn = ft * 12 + inch;
heightM = totalIn * 0.0254;
weightKg = (parseFloat(lbsEl.value) || NaN) * 0.45359237;
} else {
weightKg = parseFloat(kg2El.value) || NaN;
heightM = parseFloat(mEl.value) || NaN;
}
return { weightKg, heightM };
}
function formatNum(n,d=1){ if(typeof n !== 'number' || !isFinite(n)) return '—'; return (Math.round(n * Math.pow(10,d)) / Math.pow(10,d)).toFixed(d); }
function bmiCategoryAndColor(bmi){
if(bmi < 16) return {label:'Severely Underweight', color: zones[0].color};
if(bmi < 18.5) return {label:'Underweight', color: zones[1].color};
if(bmi < 25) return {label:'Normal', color: zones[2].color};
if(bmi < 30) return {label:'Overweight', color: zones[3].color};
if(bmi < 35) return {label:'Obesity I', color: zones[4].color};
return {label:'Obesity II', color: zones[5].color};
}
function calculate(){
const age = parseInt(ageEl.value,10);
if(!age || age < 2 || age > 120){ alert('Please enter a valid age between 2 and 120.'); return; }
const { weightKg, heightM } = toMetric();
if(!weightKg || !heightM || weightKg <=0 || heightM <=0){ alert('Please enter valid height and weight.'); return; }
const bmi = weightKg / (heightM * heightM);
const bmiRounded = parseFloat(bmi.toFixed(1));
const cat = bmiCategoryAndColor(bmi);
// update UI
bmiValueEl.textContent = `${formatNum(bmiRounded,1)} kg/m²`;
bmiValueEl.style.color = cat.color;
bmiCatEl.textContent = `${cat.label} • Age ${age} • ${gender.charAt(0).toUpperCase() + gender.slice(1)}`;
bmiCatEl.style.color = cat.color;
// healthy weight range
const wmin = 18.5 * heightM * heightM;
const wmax = 25 * heightM * heightM;
if(unit === 'us'){
healthyRangeEl.textContent = `${formatNum(wmin*2.2046226218,1)} lbs - ${formatNum(wmax*2.2046226218,1)} lbs`;
} else {
healthyRangeEl.textContent = `${formatNum(wmin,1)} kg - ${formatNum(wmax,1)} kg`;
}
const weightAt25 = 25 * heightM * heightM;
const change = weightKg - weightAt25;
const changeRounded = parseFloat(change.toFixed(1));
if(Math.abs(changeRounded) < 0.1){
to25El.innerHTML = `<span style="color:${cat.color}">You are at BMI 25 (ideal).</span>`;
} else if(changeRounded > 0){
const text = unit==='us' ? `${formatNum(changeRounded*2.2046226218,1)} lbs` : `${formatNum(changeRounded,1)} kg`;
to25El.innerHTML = `<span style="color:${cat.color}">Lose ${text} to reach BMI 25</span>`;
} else {
const text = unit==='us' ? `${formatNum(Math.abs(changeRounded*2.2046226218),1)} lbs` : `${formatNum(Math.abs(changeRounded),1)} kg`;
to25El.innerHTML = `<span style="color:${cat.color}">Gain ${text} to reach BMI 25</span>`;
}
primeEl.textContent = formatNum(bmi / 25, 2);
ponderalEl.textContent = `${formatNum(weightKg / Math.pow(heightM,3),2)} kg/m³`;
// animate gauge: compute per-zone fill and animate
const targetSegments = computeFillSegments(bmi);
chart.data.datasets[1].backgroundColor = zones.map(z => z.color);
canvas.classList.add('visible');
animateTo(targetSegments, 1000);
}
/* -------------------------
events & init
------------------------- */
calcBtn.addEventListener('click', calculate);
clearBtn.addEventListener('click', ()=>{
ageEl.value=''; ftEl.value=''; inEl.value=''; lbsEl.value=''; cmEl.value=''; kgEl.value=''; mEl.value=''; kg2El.value='';
bmiValueEl.textContent='--'; bmiValueEl.style.color=''; bmiCatEl.textContent='—'; healthyRangeEl.textContent='—';
to25El.textContent='—'; primeEl.textContent='—'; ponderalEl.textContent='—';
canvas.classList.remove('visible');
currentSegments = zones.map(()=>0);
chart.data.datasets[1].data = currentSegments.slice();
chart.update('none');
});
/* Enter key triggers calculation */
document.querySelectorAll('input').forEach(i=>{
i.addEventListener('keydown', e => { if(e.key === 'Enter') calculate(); });
});
/* redraw after resize — Chart.js handles arcs. Ensure current segments persist */
let resizeTimer = null;
window.addEventListener('resize', ()=>{
if(resizeTimer) clearTimeout(resizeTimer);
resizeTimer = setTimeout(()=>{ chart.update('none'); }, 120);
});
Benefits of Using an Advanced BMI Calculator for Health Tracking
Switching to an Advanced BMI Calculator brings multiple benefits. First, it offers better accuracy by taking into account factors that the basic formula overlooks. This means your results are more reflective of your actual health status.
Second, it provides personalized health insights. Instead of receiving a vague “overweight” label, you get context—whether the weight comes from muscle, fat, or water retention. This helps in setting realistic fitness and nutrition goals.
Third, advanced calculators allow long-term tracking. By regularly inputting your data, you can see trends over time and measure the effectiveness of diet or exercise programs.
Fourth, it encourages early detection of health risks. For example, if your BMI is normal but your waist-to-height ratio is high, you may still be at risk for heart disease or type 2 diabetes.
Finally, it promotes health awareness. The more you understand about your body composition, the better equipped you are to make informed choices about diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes.
In short, an Advanced BMI Calculator is not just a measuring tool—it’s a personal health guide that supports smarter decisions and better outcomes.
Making Sense of the Results: Interpreting Advanced BMI Data
The power of an Advanced BMI Calculator lies in its interpretation, not just its numbers. A BMI score alone is a starting point, but advanced tools give you layered results.
For example:
- A normal BMI with a high waist-to-height ratio may indicate excess abdominal fat—a key risk factor for metabolic diseases.
- A high BMI with a low body fat percentage might simply reflect high muscle mass, especially for athletes.
- Ethnicity-specific thresholds could flag risks earlier for some groups.
To make sense of these results, focus on patterns, not single readings. If your results consistently show a high waist-to-hip ratio, that’s a stronger health indicator than a slightly high BMI.
It’s also important to remember that results are guidelines, not medical diagnoses. They should prompt further evaluation, either by self-monitoring or consulting a healthcare provider.
Ultimately, the goal is to use the data proactively—to design a diet, fitness routine, and lifestyle changes that align with your specific health profile.
Limitations and Important Considerations Before Using a BMI Tool
Even the most advanced BMI calculators have limitations. They’re based on formulas and statistical averages, which means they can’t replace professional medical testing.
One issue is measurement accuracy. Self-reported height, weight, or waist measurements can introduce errors that affect results. Also, calculators cannot account for factors like bone density, hydration levels, or hormonal imbalances.
Another consideration is that population-based adjustments may still generalize results. While ethnicity-specific data helps, it can’t capture every individual variation.
Also, these calculators only assess weight-related risks, not other vital health indicators such as blood pressure, cholesterol levels, or mental well-being.
The best approach is to use an Advanced BMI Calculator alongside other health assessments—like DEXA scans, blood tests, and medical check-ups. This ensures you’re getting a complete picture of your health, rather than relying on a single tool.
Conclusion: Why an Advanced BMI Calculator Should Be Part of Your Wellness Journey
The Advanced BMI Calculator is more than a number-crunching tool—it’s a health companion. By considering factors beyond just height and weight, it provides personalized, accurate, and actionable insights into your wellness.
Whether you’re starting a weight-loss plan, maintaining your current health, or aiming for peak athletic performance, this tool can guide you toward better decisions. While it shouldn’t replace professional advice, it can be your first checkpoint for understanding where you stand and what steps to take next.
In today’s world, where health awareness is more important than ever, the Advanced BMI Calculator gives you the knowledge and motivation to take charge of your fitness journey.
FAQs
What is an Advanced BMI Calculator?
An Advanced BMI Calculator is an upgraded version of the standard Body Mass Index tool. It considers additional factors like age, gender, waist circumference, and body fat percentage to give a more accurate picture of your health status.
How is BMI calculated?
The basic BMI formula is: BMI = weight (kg) ÷ [height (m)]². An advanced calculator enhances this by adding other health metrics for better accuracy.
Why is an Advanced BMI Calculator more accurate than the traditional one?
It accounts for variables the traditional formula ignores, such as muscle mass, fat distribution, and demographic factors, reducing the risk of misclassification.
Can BMI be wrong?
Yes. Standard BMI often misclassifies athletes or people with high muscle mass as overweight. Advanced calculators help minimize such errors.
What extra data does an Advanced BMI Calculator use?
It can include waist-to-height ratio, body fat percentage, activity level, and ethnicity-based health ranges.
Who should use an Advanced BMI Calculator?
Anyone tracking health or fitness, especially athletes, people with unique body types, or those seeking a personalized health assessment.
Is BMI enough to measure health?
No. While useful, BMI should be paired with other metrics like blood pressure, cholesterol, and professional health assessments.
How often should I check my BMI?
Checking every 3–6 months is ideal, unless you’re on a weight-loss or fitness plan, in which case monthly tracking is fine.
Can I create a BMI Calculator using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript?
Yes. You can design the layout with HTML, style it with CSS, and add the calculation logic with JavaScript.
Is the Advanced BMI Calculator a replacement for medical advice?
No. It’s a helpful self-assessment tool but should not replace advice from a qualified healthcare professional.
Share on Social Media
Related Articles
How to Design Agency Website Using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript
Learn how to build a stunning, responsive design agency website using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. This beginner-friendly guide covers planning,
How to Design a Website with Background Image Slider
Learn how to create a stunning, responsive background image slider for your website using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Follow our
Responsive Website Homepage Design Using HTML and CSS
Learn how to create a responsive website homepage using HTML and CSS. This step-by-step guide covers mobile-friendly layouts, styling tips,